Wondering how to fix 400 bad requests? You’re at the right place.
As a WordPress website owner, you know how frustrating it can be when your website fails to load and keeps showing 400 bad request error messages on the screen.
This could happen when the server is unable to process the request from the web browser and sends the HTTP response status code 400, indicating an issue on the client’s (browser) side.
Fortunately, HTTP status 400 bad request is not a serious issue and is quite easy to fix in many ways.
In this article, we’ll explore what 400 bad requests mean for your website and go through various proven methods on how to fix 400 bad requests on Google Chrome.
Stay ahead of the curve with our exclusive insights and analysis on the latest WordPress trends and techniques - subscribe to our newsletter today.
What is a 400 Bad Request?
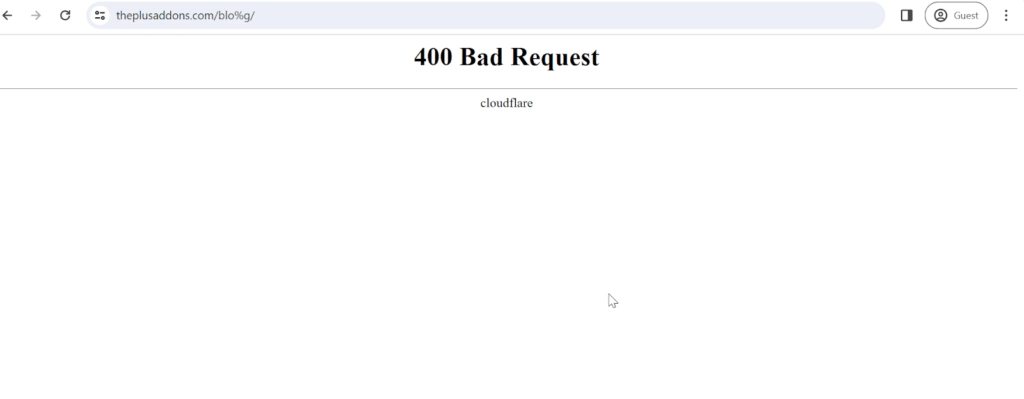
Here’s how a 400 bad request page looks in Google Chrome browser
The HTTP 400 bad request error occurs when the web server is unable to understand or process the request sent through your browser.
It is one of the HTTP 4xx series errors, known as client errors, as they are caused by an issue from the client side – the browser or the local device – instead of the hosting provider.
Other than that, the 4xx HTTP errors series includes the following-
- 400 Bad Requests: The web server is unable to process the request
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication not provided
- 402 Payments Required: Payment required to access the requested source
- 403 Forbidden: The server denies access, or the browser does not have permission to make the request
- 404 Not Found: The page requested by the browser cannot be found or does not exist
- 405 Method Not Allowed: The particular request is not supported or authorized
- 406 Not Acceptable: The server is unable to offer a response in the browser’s requested format
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required: Lack of authentication from the proxy server
- 408 Request Timeout: The server timeout was due to a slow client request, so the server terminated the connection.
- 409 Conflict: It indicates a conflict with the current state of the source
- 410 Gone: The page requested does not exist or has been deleted manually
Also, there are 28 HTTP 4xx code errors in total, but these are the most common you will encounter.
Are you facing permission access issues to the website? Here’s a quick guide on how to Fix “Sorry You Are Not Allowed to Access This Page” Error.
What Causes the 400 Bad Request Error?
HTTP status 400 bad requests typically occur due to an issue with the browser or the local device you’re using to access your website.
Some of the most common causes of 400 bad request errors include-
- Corrupted browser cache: Corrupted browser cache or expired browser cookies may cause the server to misunderstand the request and display the 400 status code.
- Invalid request syntax: Malformed request syntax, such as typing errors, may cause the server to misinterpret the request.
- Large file size: If you are uploading a file size that is too large and exceeds the maximum upload limit, the server might not be able to process your request.
- Invalid URL characters: Mistyped URLs or invalid characters, such as incorrect character escaping or encoding errors in the URL, can result in a 400 error.
- Incorrect request routing: A mismatch of data between browser input and server reception due to incorrect routing of requests can lead to errors.
Working Methods to Fix 400 Bad Request Errors
1. Use Another Browser
The first step is to check your browser. There might be times when browser issues send invalid HTTP requests to website servers.
An effective way to verify this is to try the website URL on a different browser.
If the website works in other browsers, you will need to troubleshoot the first browser by resetting browser settings and preferences, deactivating browser extensions, or re-installing the browser.
However, if the website doesn’t work even in other browsers either, you’ll need to try out some of the other methods mentioned here.
2. Verify the URL
Now, if your website isn’t working in any browser, it might be caused by an error with the URL.
It is quite a common mistake to mistype a URL when entering it manually. Double-check the URL you’ve entered for any typos, incorrect use of special characters, or invalid encoding.
Check that the domain name for the specific website page is typed correctly and separated with forward slashes.
If the URL has special characters like percentage (%) or hyphen (-), ensure they are placed correctly, as omission or incorrect placement can lead to issues.
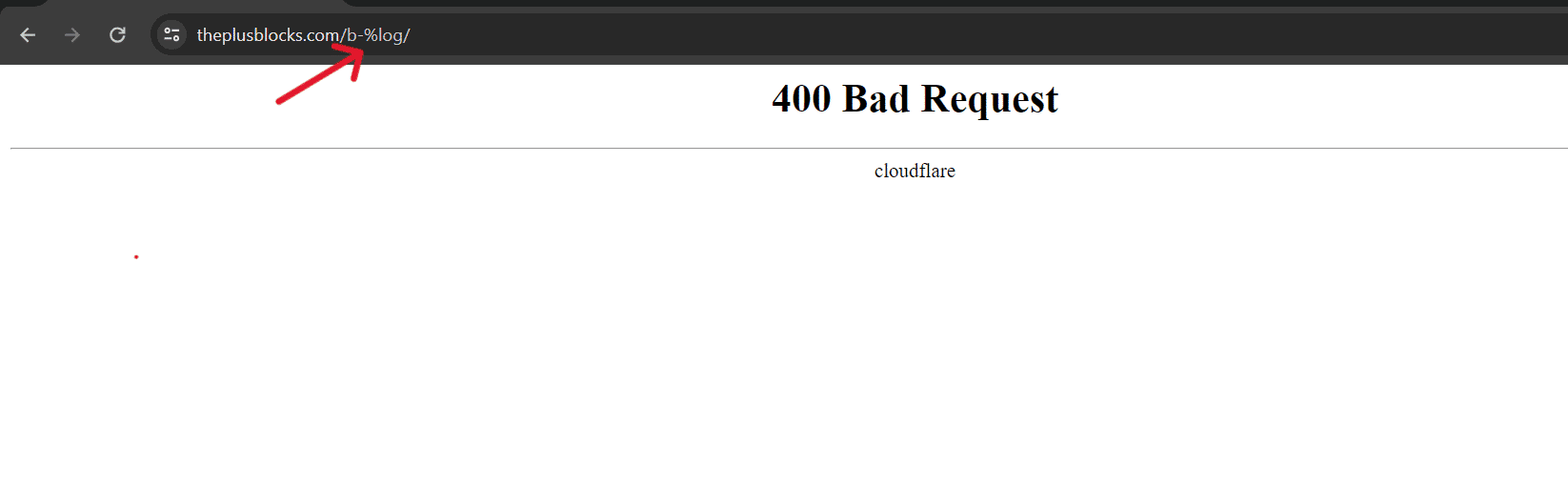
3. Refresh the Page
Another easy and quick way to fix the 400 bad request error is to refresh the web page.
By refreshing the web page, you’re essentially telling the browser to ignore any cache files of the page it has and request new files from the server.
Use these common keyboard shortcuts to refresh your web page-
- Chrome on Mac: Command + Shift + R
- Google Chrome on Windows: ctrl + R or Ctrl + F5
- Safari: Command + Option + R
- Firefox on Windows: ctrl + F5
- Firefox on Mac: Command + Shift + R
- Microsoft Edge: Ctrl + F5
4. Delete Browser Cache
Your browser saves website data files such as texts and images locally on your device.
This helps the browser access the site data faster the next time you visit the website, and it results in faster loading.
However, if any locally stored files are corrupted, it can lead to browser errors. So, you will need to clear your browser cache to fix the 400 bad request error.
If you are using Google Chrome, here’s how you can do it-
- In Chrome, tap on the three-dot icon in the top right-hand corner.
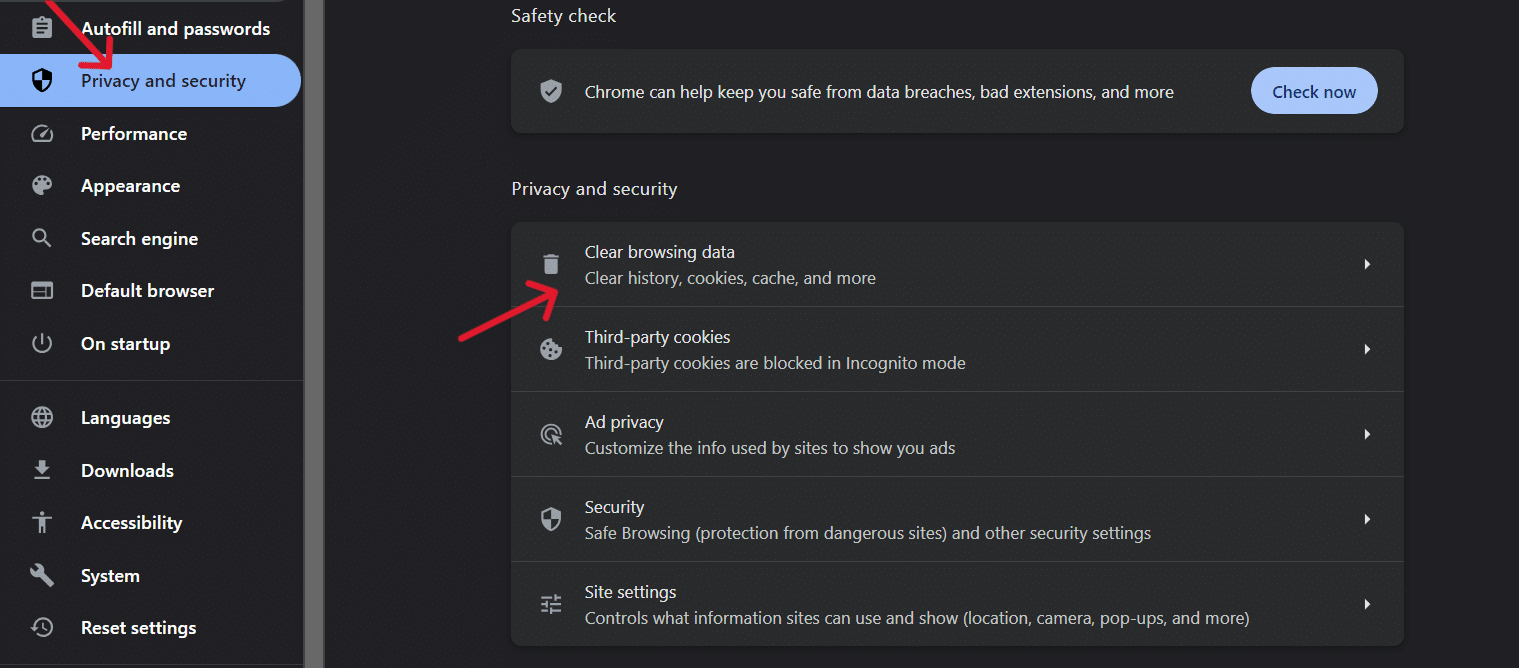
- Go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Clear Browsing Data from the drop-down menu
- In the popup that follows, check the Cached images and files option and click on Clear data.
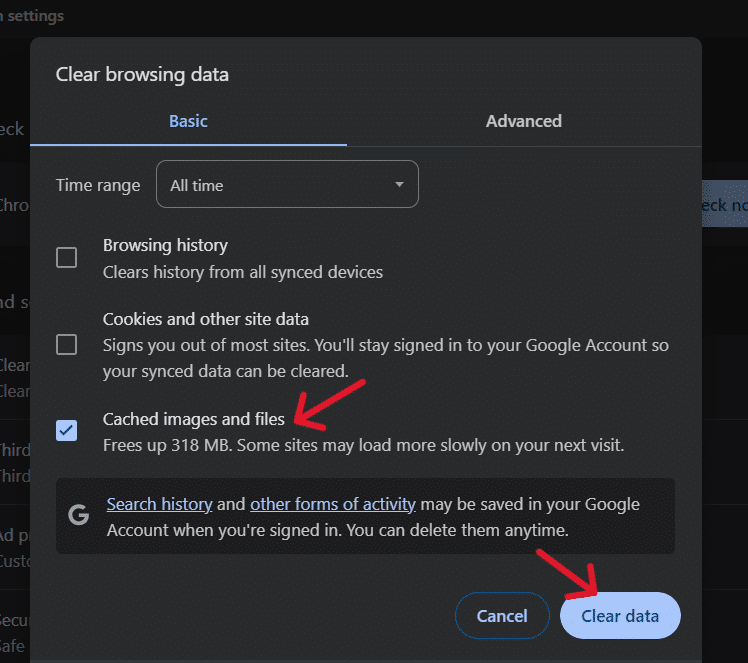
After clearing the cache, try accessing the website again. If the error persists, check out other troubleshooting methods.
Improve your site’s performance and caching storage with a WordPress caching plugin. Check out the 5 Best WordPress Caching Plugins to help speed up your site.
5. Check File Size
Web servers typically restrict the maximum file size one can upload to manage data transfers effectively.
In such a case, if you are trying to upload a file that exceeds the server file size limitation, it will lead to 400 bad request issues.
To verify if the server error is due to a file size issue, upload a smaller file size.
If it is uploaded successfully, the original file was too large, and you’ll have to resize it to upload it to the website.
Plenty of resources available online can help you compress large image files, audio, and video files.
To check the file size limit in WordPress, go to Media > Library > Add New on the WordPress dashboard and check the size limit.
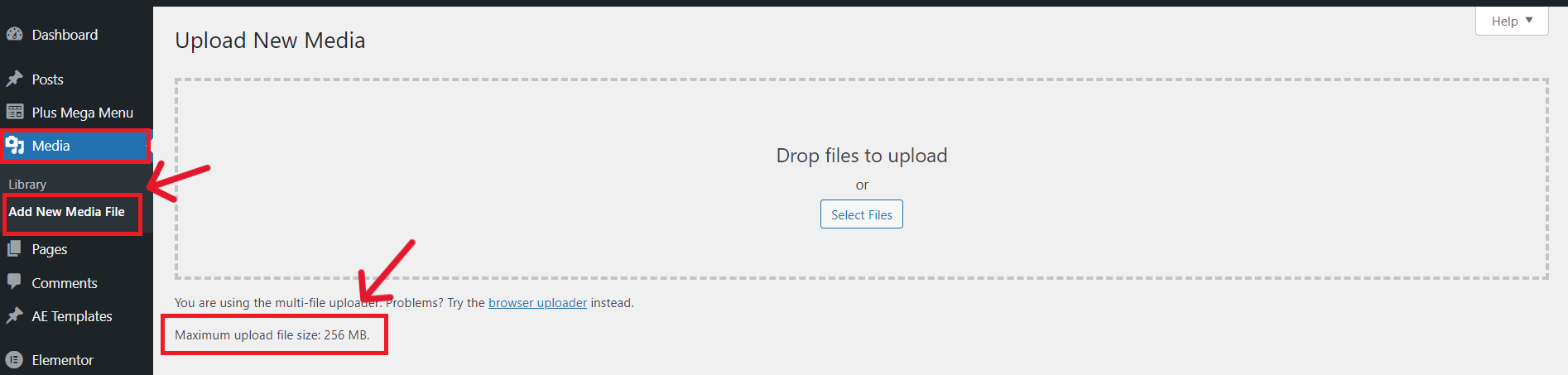
Worried about the website displaying blurred images? Learn How to Fix Blurry Images in WordPress with 6 Proven Methods.
6. Disable Browser Extensions
Browser extensions are an easy way to add unique functions to your browser.
However, sometimes, poorly coded extensions can also conflict with the working of certain websites, causing HTTP 400 bad request errors.
If you’re using any browser extensions, consider disabling them temporarily to see if it resolves the issue.
Here’s how you can do this in Google Chrome-
- Click on the three dots in the right corner at the top for Settings
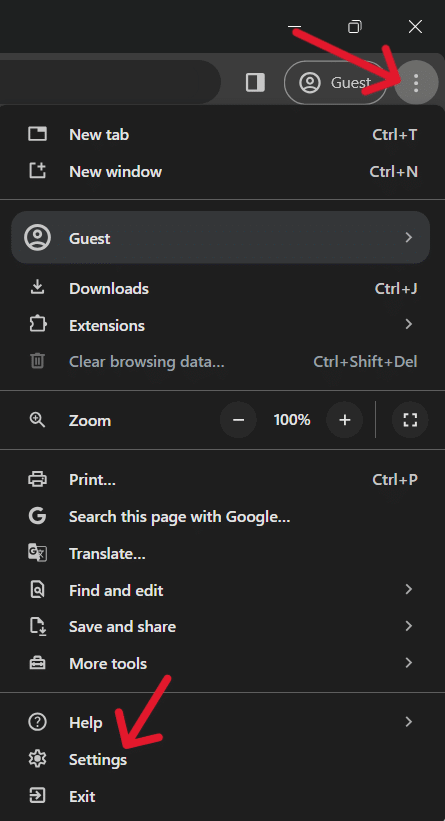
- Click on Extensions
- You will see the list of active browser extensions
- Turn the toggle off for each extension
After turning off the extensions, reload the web page. If the 400 error is resolved, this means any of the extensions were causing the problem.
Next, re-enable each extension individually and refresh the website after each to see which of the browser extensions was causing the HTTP status 400 bad request.
Once you find the problematic extension, try updating it.
But if the issue persists, remove the browser extension.
7. Remove Corrupted or Invalid Cookies
Cookies are small files that track and store personalized details like the user’s session history, site preferences, and login details, and they are stored on your device.
As with browser cache, corrupted or outdated cookies can also affect your website and cause 400 bad request errors.
Additionally, if the cookie data sent by the browser exceeds the permitted file size, it can also display a specific status code such as 400 Bad Request – Request Header or Cookie Too Large.
To clear the website cookies, go to Google Chrome > Settings > Privacy & Security > Clear Browsing Data.
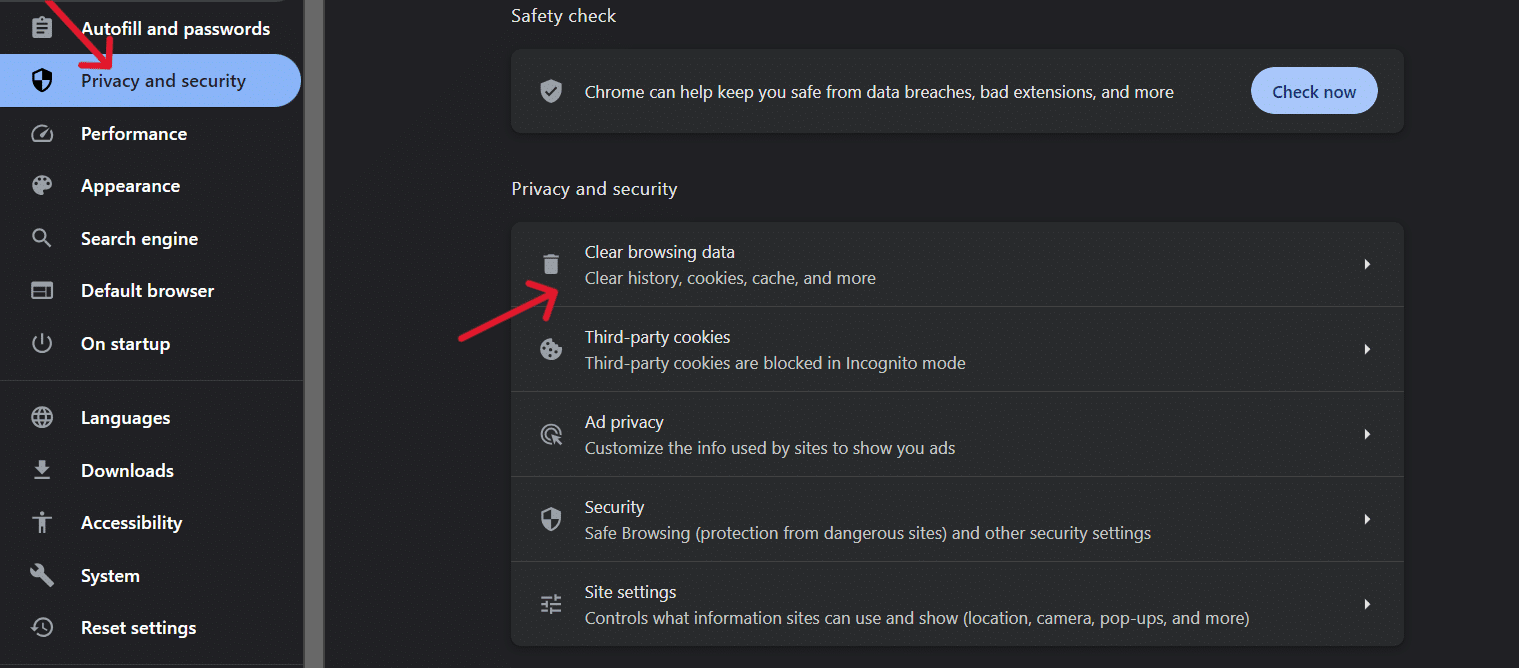
In the popup window, check Cookie and other site data and click on Clear Data.
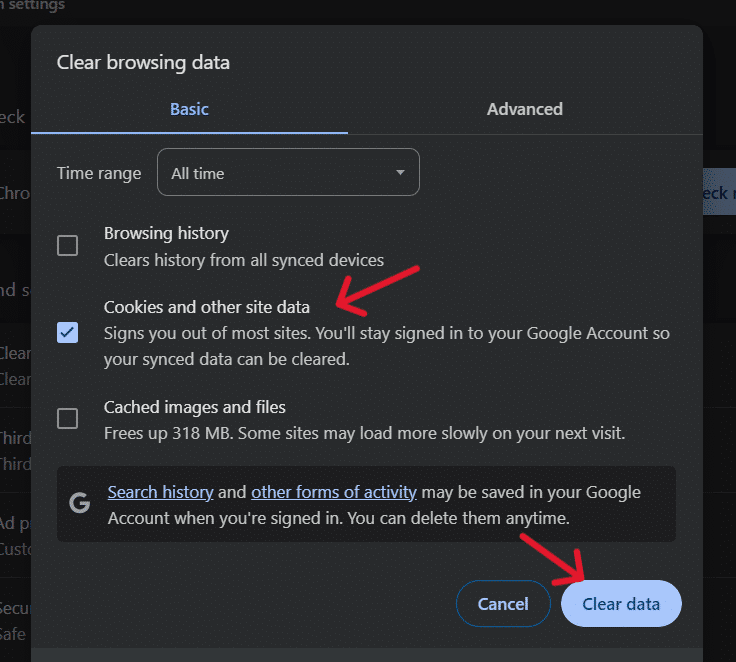
Restart Google Chrome and visit your website to see if the issue is resolved.
Are you frustrated with your website issues? Here are the 10 Common WordPress Mistakes to Avoid (with Solutions).
Get our best WordPress tips, tricks, and tutorials delivered straight to your inbox - Subscribe to our Monthly Email newsletter Today.
Wrapping Up
The HTTP status 400 bad requests is a common issue that can occur when the server cannot process browser requests.
Corrupted browser cache and cookies, invalid URL, incorrect request routing, or large file sizes can often result in code 400 message bad request syntax.
This article explored 7 proven and easy methods to fix the 400 bad request issues on your WordPress website.
If you’re using Gutenberg editor to build your website, we recommend checking out The Plus Blocks for Gutenberg – a complete Gutenberg toolkit with 85+ unique blocks to enhance the functionality of your Gutenberg page builder.

FAQs on Fixing 400 Bad Request Errors
Is the 400 bad request error a client-side or server-side issue?
400 bad request error is a client-side error, which means it occurs due to any issue with the browser or the local device.
What are the common causes of a 400 bad request error?
Invalid request syntax, incorrect URL characters, corrupted or outdated browser cache and cookies, incorrect request routing, and large file size upload are some of the common causes that can result in the HTTP 400 bad request status error.
What are some best practices for avoiding a 400 bad request error?
To avoid 400 bad request errors, make sure to update browser cookies and clean corrupted cache data. Also, troubleshooting your browser, disabling any corrupted browser extensions, and checking for large file sizes before uploading can help avoid or resolve this issue.
Which tools can help me debug a 400 bad request error?
Browser developer tools such as Chrome DevTools can help you debug 400 bad request errors.
How to fix 400 bad requests on Google Chrome?
To fix 400 bad request errors on Google Chrome, try clearing the browser cache and cookies, as they can be outdated. Also, try turning off the browser extensions, check if the file size exceeds the acceptable limit, and double-check the URL to fix the website error.


